
🚀 Work With Us
Private Coaching
Language Editing
Qualitative Coding
✨ Free Resources
Templates & Tools
Short Courses
Articles & Videos

How To Write A Dissertation Or Thesis
8 Straightforward Steps + Examples
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) Expert Reviewed By: Dr Eunice Rautenbach | June 2020

How To Write A Dissertation: 8 Steps
- Clearly understand what a dissertation (or thesis) is
- Find a unique and valuable research topic
- Craft a convincing research proposal
- Write up a strong introduction chapter
- Review the existing literature and compile a literature review
- Design a rigorous research strategy and undertake your own research
- Present the findings of your research
- Draw a conclusion and discuss the implications

Step 1: Understand exactly what a dissertation is
This probably sounds like a no-brainer, but all too often, students come to us for help with their research and the underlying issue is that they don’t fully understand what a dissertation (or thesis) actually is.
So, what is a dissertation?
At its simplest, a dissertation or thesis is a formal piece of research , reflecting the standard research process . But what is the standard research process, you ask? The research process involves 4 key steps:
- Ask a very specific, well-articulated question (s) (your research topic)
- See what other researchers have said about it (if they’ve already answered it)
- If they haven’t answered it adequately, undertake your own data collection and analysis in a scientifically rigorous fashion
- Answer your original question(s), based on your analysis findings

In short, the research process is simply about asking and answering questions in a systematic fashion . This probably sounds pretty obvious, but people often think they’ve done “research”, when in fact what they have done is:
- Started with a vague, poorly articulated question
- Not taken the time to see what research has already been done regarding the question
- Collected data and opinions that support their gut and undertaken a flimsy analysis
- Drawn a shaky conclusion, based on that analysis
If you want to see the perfect example of this in action, look out for the next Facebook post where someone claims they’ve done “research”… All too often, people consider reading a few blog posts to constitute research. Its no surprise then that what they end up with is an opinion piece, not research. Okay, okay – I’ll climb off my soapbox now.
The key takeaway here is that a dissertation (or thesis) is a formal piece of research, reflecting the research process. It’s not an opinion piece , nor a place to push your agenda or try to convince someone of your position. Writing a good dissertation involves asking a question and taking a systematic, rigorous approach to answering it.
If you understand this and are comfortable leaving your opinions or preconceived ideas at the door, you’re already off to a good start!
⚡ GET THE FREE TEMPLATE ⚡
Fast-track your research with our award-winning Dissertation Template .
Download Now 📂
Step 2: Find a unique, valuable research topic
As we saw, the first step of the research process is to ask a specific, well-articulated question. In other words, you need to find a research topic that asks a specific question or set of questions (these are called research questions ). Sounds easy enough, right? All you’ve got to do is identify a question or two and you’ve got a winning research topic. Well, not quite…
A good dissertation or thesis topic has a few important attributes. Specifically, a solid research topic should be:
Let’s take a closer look at these:
Attribute #1: Clear
Your research topic needs to be crystal clear about what you’re planning to research, what you want to know, and within what context. There shouldn’t be any ambiguity or vagueness about what you’ll research.
Here’s an example of a clearly articulated research topic:
An analysis of consumer-based factors influencing organisational trust in British low-cost online equity brokerage firms.
As you can see in the example, its crystal clear what will be analysed (factors impacting organisational trust), amongst who (consumers) and in what context (British low-cost equity brokerage firms, based online).
Need a helping hand?
Attribute #2: Unique
Your research should be asking a question(s) that hasn’t been asked before, or that hasn’t been asked in a specific context (for example, in a specific country or industry).
For example, sticking organisational trust topic above, it’s quite likely that organisational trust factors in the UK have been investigated before, but the context (online low-cost equity brokerages) could make this research unique. Therefore, the context makes this research original.
One caveat when using context as the basis for originality – you need to have a good reason to suspect that your findings in this context might be different from the existing research – otherwise, there’s no reason to warrant researching it.
Attribute #3: Important
Simply asking a unique or original question is not enough – the question needs to create value. In other words, successfully answering your research questions should provide some value to the field of research or the industry. You can’t research something just to satisfy your curiosity. It needs to make some form of contribution either to research or industry.
For example, researching the factors influencing consumer trust would create value by enabling businesses to tailor their operations and marketing to leverage factors that promote trust. In other words, it would have a clear benefit to industry.
So, how do you go about finding a unique and valuable research topic? We explain that in detail in this video post – How To Find A Research Topic . Yeah, we’ve got you covered 😊
Step 3: Write a convincing research proposal
Once you’ve pinned down a high-quality research topic, the next step is to convince your university to let you research it. No matter how awesome you think your topic is, it still needs to get the rubber stamp before you can move forward with your research. The research proposal is the tool you’ll use for this job.
So, what’s in a research proposal?
The main “job” of a research proposal is to convince your university, advisor or committee that your research topic is worthy of approval. But convince them of what? Well, this varies from university to university, but generally, they want to see that:
- You have a clearly articulated, unique and important topic (this might sound familiar…)
- You’ve done some initial reading of the existing literature relevant to your topic (i.e. a literature review)
- You have a provisional plan in terms of how you will collect data and analyse it (i.e. a methodology)
At the proposal stage, it’s (generally) not expected that you’ve extensively reviewed the existing literature , but you will need to show that you’ve done enough reading to identify a clear gap for original (unique) research. Similarly, they generally don’t expect that you have a rock-solid research methodology mapped out, but you should have an idea of whether you’ll be undertaking qualitative or quantitative analysis , and how you’ll collect your data (we’ll discuss this in more detail later).
Long story short – don’t stress about having every detail of your research meticulously thought out at the proposal stage – this will develop as you progress through your research. However, you do need to show that you’ve “done your homework” and that your research is worthy of approval .
So, how do you go about crafting a high-quality, convincing proposal? We cover that in detail in this video post – How To Write A Top-Class Research Proposal . We’ve also got a video walkthrough of two proposal examples here .
Step 4: Craft a strong introduction chapter
Once your proposal’s been approved, its time to get writing your actual dissertation or thesis! The good news is that if you put the time into crafting a high-quality proposal, you’ve already got a head start on your first three chapters – introduction, literature review and methodology – as you can use your proposal as the basis for these.
Handy sidenote – our free dissertation & thesis template is a great way to speed up your dissertation writing journey.
What’s the introduction chapter all about?
The purpose of the introduction chapter is to set the scene for your research (dare I say, to introduce it…) so that the reader understands what you’ll be researching and why it’s important. In other words, it covers the same ground as the research proposal in that it justifies your research topic.
What goes into the introduction chapter?
This can vary slightly between universities and degrees, but generally, the introduction chapter will include the following:
- A brief background to the study, explaining the overall area of research
- A problem statement , explaining what the problem is with the current state of research (in other words, where the knowledge gap exists)
- Your research questions – in other words, the specific questions your study will seek to answer (based on the knowledge gap)
- The significance of your study – in other words, why it’s important and how its findings will be useful in the world
As you can see, this all about explaining the “what” and the “why” of your research (as opposed to the “how”). So, your introduction chapter is basically the salesman of your study, “selling” your research to the first-time reader and (hopefully) getting them interested to read more.

Step 5: Undertake an in-depth literature review
As I mentioned earlier, you’ll need to do some initial review of the literature in Steps 2 and 3 to find your research gap and craft a convincing research proposal – but that’s just scratching the surface. Once you reach the literature review stage of your dissertation or thesis, you need to dig a lot deeper into the existing research and write up a comprehensive literature review chapter.
What’s the literature review all about?
There are two main stages in the literature review process:
Literature Review Step 1: Reading up
The first stage is for you to deep dive into the existing literature (journal articles, textbook chapters, industry reports, etc) to gain an in-depth understanding of the current state of research regarding your topic. While you don’t need to read every single article, you do need to ensure that you cover all literature that is related to your core research questions, and create a comprehensive catalogue of that literature , which you’ll use in the next step.
Reading and digesting all the relevant literature is a time consuming and intellectually demanding process. Many students underestimate just how much work goes into this step, so make sure that you allocate a good amount of time for this when planning out your research. Thankfully, there are ways to fast track the process – be sure to check out this article covering how to read journal articles quickly .

Literature Review Step 2: Writing up
Once you’ve worked through the literature and digested it all, you’ll need to write up your literature review chapter. Many students make the mistake of thinking that the literature review chapter is simply a summary of what other researchers have said. While this is partly true, a literature review is much more than just a summary. To pull off a good literature review chapter, you’ll need to achieve at least 3 things:
- You need to synthesise the existing research , not just summarise it. In other words, you need to show how different pieces of theory fit together, what’s agreed on by researchers, what’s not.
- You need to highlight a research gap that your research is going to fill. In other words, you’ve got to outline the problem so that your research topic can provide a solution.
- You need to use the existing research to inform your methodology and approach to your own research design. For example, you might use questions or Likert scales from previous studies in your your own survey design .
As you can see, a good literature review is more than just a summary of the published research. It’s the foundation on which your own research is built, so it deserves a lot of love and attention. Take the time to craft a comprehensive literature review with a suitable structure .
But, how do I actually write the literature review chapter, you ask? We cover that in detail in this video post .
Step 6: Carry out your own research
Once you’ve completed your literature review and have a sound understanding of the existing research, its time to develop your own research (finally!). You’ll design this research specifically so that you can find the answers to your unique research question.
There are two steps here – designing your research strategy and executing on it:
1 – Design your research strategy
The first step is to design your research strategy and craft a methodology chapter . I won’t get into the technicalities of the methodology chapter here, but in simple terms, this chapter is about explaining the “how” of your research. If you recall, the introduction and literature review chapters discussed the “what” and the “why”, so it makes sense that the next point to cover is the “how” –that’s what the methodology chapter is all about.
In this section, you’ll need to make firm decisions about your research design. This includes things like:
- Your research philosophy (e.g. positivism or interpretivism )
- Your overall methodology (e.g. qualitative , quantitative or mixed methods)
- Your data collection strategy (e.g. interviews , focus groups, surveys)
- Your data analysis strategy (e.g. content analysis , correlation analysis, regression)
If these words have got your head spinning, don’t worry! We’ll explain these in plain language in other posts. It’s not essential that you understand the intricacies of research design (yet!). The key takeaway here is that you’ll need to make decisions about how you’ll design your own research, and you’ll need to describe (and justify) your decisions in your methodology chapter.
2 – Execute: Collect and analyse your data
Once you’ve worked out your research design, you’ll put it into action and start collecting your data. This might mean undertaking interviews, hosting an online survey or any other data collection method. Data collection can take quite a bit of time (especially if you host in-person interviews), so be sure to factor sufficient time into your project plan for this. Oftentimes, things don’t go 100% to plan (for example, you don’t get as many survey responses as you hoped for), so bake a little extra time into your budget here.
Once you’ve collected your data, you’ll need to do some data preparation before you can sink your teeth into the analysis. For example:
- If you carry out interviews or focus groups, you’ll need to transcribe your audio data to text (i.e. a Word document).
- If you collect quantitative survey data, you’ll need to clean up your data and get it into the right format for whichever analysis software you use (for example, SPSS, R or STATA).
Once you’ve completed your data prep, you’ll undertake your analysis, using the techniques that you described in your methodology. Depending on what you find in your analysis, you might also do some additional forms of analysis that you hadn’t planned for. For example, you might see something in the data that raises new questions or that requires clarification with further analysis.
The type(s) of analysis that you’ll use depend entirely on the nature of your research and your research questions. For example:
- If your research if exploratory in nature, you’ll often use qualitative analysis techniques .
- If your research is confirmatory in nature, you’ll often use quantitative analysis techniques
- If your research involves a mix of both, you might use a mixed methods approach
Again, if these words have got your head spinning, don’t worry! We’ll explain these concepts and techniques in other posts. The key takeaway is simply that there’s no “one size fits all” for research design and methodology – it all depends on your topic, your research questions and your data. So, don’t be surprised if your study colleagues take a completely different approach to yours.

Step 7: Present your findings
Once you’ve completed your analysis, it’s time to present your findings (finally!). In a dissertation or thesis, you’ll typically present your findings in two chapters – the results chapter and the discussion chapter .
What’s the difference between the results chapter and the discussion chapter?
While these two chapters are similar, the results chapter generally just presents the processed data neatly and clearly without interpretation, while the discussion chapter explains the story the data are telling – in other words, it provides your interpretation of the results.
For example, if you were researching the factors that influence consumer trust, you might have used a quantitative approach to identify the relationship between potential factors (e.g. perceived integrity and competence of the organisation) and consumer trust. In this case:
- Your results chapter would just present the results of the statistical tests. For example, correlation results or differences between groups. In other words, the processed numbers.
- Your discussion chapter would explain what the numbers mean in relation to your research question(s). For example, Factor 1 has a weak relationship with consumer trust, while Factor 2 has a strong relationship.
Depending on the university and degree, these two chapters (results and discussion) are sometimes merged into one , so be sure to check with your institution what their preference is. Regardless of the chapter structure, this section is about presenting the findings of your research in a clear, easy to understand fashion.
Importantly, your discussion here needs to link back to your research questions (which you outlined in the introduction or literature review chapter). In other words, it needs to answer the key questions you asked (or at least attempt to answer them).
For example, if we look at the sample research topic:
In this case, the discussion section would clearly outline which factors seem to have a noteworthy influence on organisational trust. By doing so, they are answering the overarching question and fulfilling the purpose of the research .
Step 8: The Final Step Draw a conclusion and discuss the implications
Last but not least, you’ll need to wrap up your research with the conclusion chapter . In this chapter, you’ll bring your research full circle by highlighting the key findings of your study and explaining what the implications of these findings are.
What exactly are key findings? The key findings are those findings which directly relate to your original research questions and overall research objectives (which you discussed in your introduction chapter). The implications, on the other hand, explain what your findings mean for industry, or for research in your area.
Sticking with the consumer trust topic example, the conclusion might look something like this:
Key findings
This study set out to identify which factors influence consumer-based trust in British low-cost online equity brokerage firms. The results suggest that the following factors have a large impact on consumer trust:
While the following factors have a very limited impact on consumer trust:
Notably, within the 25-30 age groups, Factors E had a noticeably larger impact, which may be explained by…
Implications
The findings having noteworthy implications for British low-cost online equity brokers. Specifically:
The large impact of Factors X and Y implies that brokers need to consider….
The limited impact of Factor E implies that brokers need to…
As you can see, the conclusion chapter is basically explaining the “what” (what your study found) and the “so what?” (what the findings mean for the industry or research). This brings the study full circle and closes off the document.

Let’s recap – how to write a dissertation or thesis
You’re still with me? Impressive! I know that this post was a long one, but hopefully you’ve learnt a thing or two about how to write a dissertation or thesis, and are now better equipped to start your own research.
To recap, the 8 steps to writing a quality dissertation (or thesis) are as follows:
- Understand what a dissertation (or thesis) is – a research project that follows the research process.
- Find a unique (original) and important research topic
- Craft a convincing dissertation or thesis research proposal
- Write a clear, compelling introduction chapter
- Undertake a thorough review of the existing research and write up a literature review
- Undertake your own research
- Present and interpret your findings
Once you’ve wrapped up the core chapters, all that’s typically left is the abstract , reference list and appendices. As always, be sure to check with your university if they have any additional requirements in terms of structure or content.

You Might Also Like:

How To Choose A Tutor For Your Dissertation
Hiring the right tutor for your dissertation or thesis can make the difference between passing and failing. Here’s what you need to consider.

5 Signs You Need A Dissertation Helper
Discover the 5 signs that suggest you need a dissertation helper to get unstuck, finish your degree and get your life back.

Writing A Dissertation While Working: A How-To Guide
Struggling to balance your dissertation with a full-time job and family? Learn practical strategies to achieve success.

How To Review & Understand Academic Literature Quickly
Learn how to fast-track your literature review by reading with intention and clarity. Dr E and Amy Murdock explain how.

Dissertation Writing Services: Far Worse Than You Think
Thinking about using a dissertation or thesis writing service? You might want to reconsider that move. Here’s what you need to know.
📄 FREE TEMPLATES
Research Topic Ideation
Proposal Writing
Literature Review
Methodology & Analysis
Academic Writing
Referencing & Citing
Apps, Tools & Tricks
The Grad Coach Podcast
21 Comments
thankfull >>>this is very useful
Thank you, it was really helpful
unquestionably, this amazing simplified way of teaching. Really , I couldn’t find in the literature words that fully explicit my great thanks to you. However, I could only say thanks a-lot.
Great to hear that – thanks for the feedback. Good luck writing your dissertation/thesis.
This is the most comprehensive explanation of how to write a dissertation. Many thanks for sharing it free of charge.
Very rich presentation. Thank you
Thanks Derek Jansen|GRADCOACH, I find it very useful guide to arrange my activities and proceed to research!
Thank you so much for such a marvelous teaching .I am so convinced that am going to write a comprehensive and a distinct masters dissertation
It is an amazing comprehensive explanation
This was straightforward. Thank you!
I can say that your explanations are simple and enlightening – understanding what you have done here is easy for me. Could you write more about the different types of research methods specific to the three methodologies: quan, qual and MM. I look forward to interacting with this website more in the future.
Thanks for the feedback and suggestions 🙂
Hello, your write ups is quite educative. However, l have challenges in going about my research questions which is below; *Building the enablers of organisational growth through effective governance and purposeful leadership.*
Very educating.
Just listening to the name of the dissertation makes the student nervous. As writing a top-quality dissertation is a difficult task as it is a lengthy topic, requires a lot of research and understanding and is usually around 10,000 to 15000 words. Sometimes due to studies, unbalanced workload or lack of research and writing skill students look for dissertation submission from professional writers.
Thank you 💕😊 very much. I was confused but your comprehensive explanation has cleared my doubts of ever presenting a good thesis. Thank you.
thank you so much, that was so useful
Hi. Where is the excel spread sheet ark?
could you please help me look at your thesis paper to enable me to do the portion that has to do with the specification
my topic is “the impact of domestic revenue mobilization.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Submit Comment
- Print Friendly
- How it works
"Christmas Offer"
Terms & conditions.
As the Christmas season is upon us, we find ourselves reflecting on the past year and those who we have helped to shape their future. It’s been quite a year for us all! The end of the year brings no greater joy than the opportunity to express to you Christmas greetings and good wishes.
At this special time of year, Research Prospect brings joyful discount of 10% on all its services. May your Christmas and New Year be filled with joy.
We are looking back with appreciation for your loyalty and looking forward to moving into the New Year together.
"Claim this offer"
In unfamiliar and hard times, we have stuck by you. This Christmas, Research Prospect brings you all the joy with exciting discount of 10% on all its services.
Offer valid till 5-1-2024
We love being your partner in success. We know you have been working hard lately, take a break this holiday season to spend time with your loved ones while we make sure you succeed in your academics
Discount code: RP0996Y

Your content here...

Research Question Examples – Guide & Tips
Published by Owen Ingram at August 13th, 2021 , Revised On October 3, 2024
One of the most important parts of your research paper , thesis or dissertation is a research question. A strong research question lays the foundation for an in-depth analysis and insightful conclusions. It serves as a guide for your research paper and states what you want and which problem you want to address.
In this blog, we will cover precise and properly structured research question examples, to facilitate your understanding and help you approach your work with confidence.
What Is A Research Question Example?
A research question example is a sample that provides a deeper understanding of how to write a research question. These examples can help first-time authors comprehend the structure and components of the question.
A research question’s length depends on the topic chosen and the specific requirements of the field. However, the length should not be the main focus. The ultimate goal is to convey the main problem statement being addressed.
Importance Of Research Question
A research question is a critical component of research because of the following reasons:
- It is central to research as it guides the research design , data collection , analysis, evaluation and interpretation of the results.
- The paper relies on the research question to properly address the evaluated problem and inform readers about the research topic. Without a question, the readers and researchers may face difficulty in understanding the purpose of your research.
- It helps researchers understand the quantity and type of data needed to answer the question sufficiently.
- Moreover, it provides a framework for drawing conclusions and builds the credibility of the research design.

Research Questions for Dissertation Examples
Below are 10 examples of research questions that will enable you to develop research questions for your research. These examples will help you to check whether your chosen research questions can be addressed or whether they are too broad to find a conclusive answer.
List of Research Question Examples For Students
Effective research questions are clear and focused, and well-written. Many students struggle to craft such questions, which is why we have listed a few examples of different types of research questions. By examining these questions, students can have a clearer understanding of how to develop research questions of all disciplines.
Examples of Qualitative Research Questions
Qualitative research questions focus on specific areas of study or broader themes. They are adaptable and flexible, unlike quantitative research questions. There are certain categories of qualitative research questions such as contextual, descriptive, evaluative, explanatory and exploratory. Let’s discuss a few examples of qualitative research questions:
Example 1: What are the characteristics of ATP synthase?
Example 2: What factors contribute to homelessness in urban areas?
Example 3: What are the challenges faced by immigrants in learning a new language?
Example 4: What is the cause of increased violence among young adults?
Example 5: What are the spiritual experiences of individuals who practice medication?
Example 6: What are the experiences of patients with chronic illness in getting healthcare services?
Example 7: Is it possible that VEGF has an effect on plant photosynthesis?
Examples of Quantitative Research Questions
Quantitative research questions measure and quantify variables to identify relationships and correlations. These questions aim to answer the “how many” or “how much” aspects of a subject, and are widely used in fields that involve statistical analysis and numerical data. Here are seven examples of quantitative research questions:
Example 1: What is the correlation between sleep duration and productivity levels among office workers?
Example 2: What percentage of people in the city support the ban on plastic bags?
Example 3: What is the relationship between TikTok usage and academic performance among college students?
Example 4: What is the effect of a high-protein diet on muscle growth in fitness individuals?
Example 5: What is the relationship between social media usage and depression in young adults?
Example 6: How does the consumption of dietary fibre affect blood sugar levels in people with type 2 diabetes?
Example 7: What effect does internet speed have in increasing work productivity in the IT sector?
Constructivist Research Questions Examples
Constructive research questions are designed to explore an individual’s interaction with the world, and how they create meaning through it. They examine the process that develops an individual’s understanding, perspectives and knowledge. Here are some examples of constructivist research questions:
Example 1: How do employees learn and respond to organisational change initiatives?
Example 2: What effects do teaching methods have on student’s perception of learning?
Example 3: How do individuals create their identities in relation to their cultural backgrounds?
Example 4: What are the variables that affect an individual’s perception of justice?
Example 5: How does media shape people’s perception of social issues?
Example 6: How do students construct their understanding of complex mathematical concepts?
Example 7: What are the challenges faced by marginalised groups in media production?
Discourse Analysis Research Question Examples
Understanding how language is used to construct meaning, power dynamics and social identities in particular contexts is the main purpose of discourse analysis research questions. They are also known as discursive research questions. They aim to investigate the way language shapes ideologies and social structures. Some popular examples of discourse analysis research questions are:
Example 1: How does discourse in health advertisements promote products and services?
Example 2: How is a discourse in criminal justice policy used to shape public attitudes towards justice and punishment?
Example 3: How is national identity constructed by the usage of discourse in flags and national anthems?
Example 4: How is discourse used to confront racial stereotypes?
Example 5: How is classroom discourse used to maintain power relations among professors and students?
Example 6: How does advertising discourse construct gender stereotypes?
Example 7: How is discourse in political campaigns used to obtain support for specific candidates?
Comparative Research Questions Examples
Comparative research questions aim to identify the differences and similarities between two cases, phenomena and groups. These questions compare and contrast different variables to identify trends, practices and relationships. Let’s explore some examples to gain a better understanding:
Example 1: What are the similarities and differences in political systems between democracies and authoritarian regimes?
Example 2: What are the differences between the economic policies of developed and under-developed countries?
Example 3: How do family structures differ in various cultures?
Example 4: What are the similarities and differences in gender roles across various cultures?
Example 5: What are the similarities and differences in the prevalence of chronic diseases across various countries?
Example 6: How do literary works from different time periods compare in terms of theme and prose?
Example 7: What is the biodiversity comparison between ecosystems of various biomes?
Descriptive Research Question Examples
Descriptive research questions are questions used in research to gain a clearer picture of a particular topic or phenomenon. These questions focus on specific characteristics, conditions and attributes of the topic that is being studied. Let’s study a few examples of descriptive research questions examples:
Example 1: How does childhood trauma affect mental health?
Example 2: What is the impact of globalisation on local business?
Example 3: How does artificial intelligence affect job markets?
Example 4: What are the factors that contribute to the drop-outs in schools?
Example 5: How much do brands invest in digital marketing as compared to traditional advertising?
Example 6: What is the effect of climate change on biodiversity?
Example 7: What are the ethical limitations of genetic engineering?
Does your Research Methodology Have the Following?
Orders completed by our expert writers are
- Great Research/Sources
- Perfect Language
- Accurate Sources
If not, we can help. Our panel of experts makes sure to keep the 3 pillars of Research Methodology strong.

How Can We Help You with Research Questions?
If you are still unsure about writing dissertation research questions and perhaps want to see more examples, you might be interested in getting help from our dissertation writers.
At ResearchProspect, we have UK-qualified writers holding master’s and PhD degrees in all academic subjects. Whether you need help with only developing research questions or any other aspect of your dissertation paper, we are here to help you achieve your desired grades for an affordable price.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a research question example in psychology.
Research question examples in the field of psychology are:
- How does bipolar disorder’s initial age affect its progression and treatment?
- How does childhood trauma impact the advancement of borderline personality disorder in adulthood?
- What are the long-term psychological effects of being the victim of a violent crime?
What is a research question example in natural sciences?
Research question examples in natural sciences are:
- What are the effects of ocean acidification on the biodiversity of coral reef ecosystems?
- How does air pollution impact respiratory well-being in individuals living in polluted areas?
- What are the effects of organic and inorganic fertilisers on soil and crop health?
What are the characteristics of a well-written research question?
A good research question is focused, clear, specific and relevant to the topic and subject. It should also be researchable so that enough data can be collected to answer the question.
What are some examples of research questions in the classroom?
- How do interactive whiteboards impact student engagement?
- Does peer tutoring improve maths proficiency?
- How does classroom seating arrangement influence student participation?
- What’s the effect of gamified learning on student motivation?
- Does integrating technology in lessons enhance critical thinking skills?
- How does feedback frequency affect student performance?
What are some examples of research questions in geography?
- How does urbanisation impact local microclimates?
- What factors influence water scarcity in Region X?
- How do migration patterns correlate with economic disparities?
- What’s the relationship between deforestation and soil erosion in Area Y?
- How have coastlines changed over the past decade?
- Why are certain regions’ biodiversity hotspots?
What are three basic research questions?
The three basic types of research questions are:
- Descriptive: Seeks to depict a phenomenon or issue. E.g., “What are the symptoms of depression?”
- Relational: Investigates relationships between variables. E.g., “Is there a correlation between stress and heart disease?”
- Causal: Determines cause and effect. E.g., “Does smoking cause lung cancer?”
What are some examples of a research question?
Examples of research questions:
- How does social media influence self-esteem in adolescents?
- What are the economic impacts of climate change on agriculture?
- What factors contribute to employee job satisfaction in the tech industry?
- How does exercise frequency affect cardiovascular health?
- What is the relationship between sleep duration and academic performance in college students?
You May Also Like
Find how to write research questions with the mentioned steps required for a perfect research question. Choose an interesting topic and begin your research.
How to write a hypothesis for dissertation,? A hypothesis is a statement that can be tested with the help of experimental or theoretical research.
Let’s briefly examine the concept of research paradigms, their pillars, purposes, types, examples, and how they can be combined.
As Featured On

USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

Splash Sol LLC
- How It Works
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Research process
- Writing Strong Research Questions | Criteria & Examples
Writing Strong Research Questions | Criteria & Examples
Published on 30 October 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 12 December 2023.
A research question pinpoints exactly what you want to find out in your work. A good research question is essential to guide your research paper , dissertation , or thesis .
All research questions should be:
- Focused on a single problem or issue
- Researchable using primary and/or secondary sources
- Feasible to answer within the timeframe and practical constraints
- Specific enough to answer thoroughly
- Complex enough to develop the answer over the space of a paper or thesis
- Relevant to your field of study and/or society more broadly
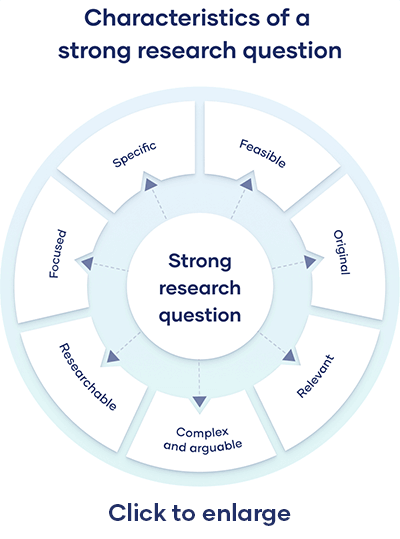
Table of contents
How to write a research question, what makes a strong research question, research questions quiz, frequently asked questions.
You can follow these steps to develop a strong research question:
- Choose your topic
- Do some preliminary reading about the current state of the field
- Narrow your focus to a specific niche
- Identify the research problem that you will address
The way you frame your question depends on what your research aims to achieve. The table below shows some examples of how you might formulate questions for different purposes.
Using your research problem to develop your research question
Note that while most research questions can be answered with various types of research , the way you frame your question should help determine your choices.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Research questions anchor your whole project, so it’s important to spend some time refining them. The criteria below can help you evaluate the strength of your research question.
Focused and researchable
Feasible and specific, complex and arguable, relevant and original.
The way you present your research problem in your introduction varies depending on the nature of your research paper . A research paper that presents a sustained argument will usually encapsulate this argument in a thesis statement .
A research paper designed to present the results of empirical research tends to present a research question that it seeks to answer. It may also include a hypothesis – a prediction that will be confirmed or disproved by your research.
As you cannot possibly read every source related to your topic, it’s important to evaluate sources to assess their relevance. Use preliminary evaluation to determine whether a source is worth examining in more depth.
This involves:
- Reading abstracts , prefaces, introductions , and conclusions
- Looking at the table of contents to determine the scope of the work
- Consulting the index for key terms or the names of important scholars
An essay isn’t just a loose collection of facts and ideas. Instead, it should be centered on an overarching argument (summarised in your thesis statement ) that every part of the essay relates to.
The way you structure your essay is crucial to presenting your argument coherently. A well-structured essay helps your reader follow the logic of your ideas and understand your overall point.
A research hypothesis is your proposed answer to your research question. The research hypothesis usually includes an explanation (‘ x affects y because …’).
A statistical hypothesis, on the other hand, is a mathematical statement about a population parameter. Statistical hypotheses always come in pairs: the null and alternative hypotheses. In a well-designed study , the statistical hypotheses correspond logically to the research hypothesis.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, December 12). Writing Strong Research Questions | Criteria & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 23 December 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/the-research-process/research-question/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a research proposal | examples & templates, how to write a results section | tips & examples, what is a research methodology | steps & tips.
- Our Mission
- Code of Conduct
- The Consultants
- Hours and Locations
- Apply to Become a Consultant
- Make an Appointment
- Face-to-Face Appointments
- Zoom Appointments
- Written Feedback Appointments
- Support for Writers with Disabilities
- Policies and Restrictions
- Upcoming Workshops
- Class Workshops
- Meet the Consultants
- Writing Center Quick Guides
- Citation Resources
- Helpful Links
- Video Resources
- Login or Register
- Graduate Writing Consultations
- Thesis and Dissertation Consultations
- Weekly Write-Ins
- ESOL Graduate Peer Feedback Groups
- Setting Up Your Own Writing Group
- Writing Resources for Graduate Students
- Support for Multilingual Students
- ESOL Opt-In Program
- About Our Consulting Services
- Promote Us to Your Students
- Recommend Consultants
How to Write a Research Question
What is a research question? A research question is the question around which you center your research. It should be:
- clear : it provides enough specifics that one’s audience can easily understand its purpose without needing additional explanation.
- focused : it is narrow enough that it can be answered thoroughly in the space the writing task allows.
- concise : it is expressed in the fewest possible words.
- complex : it is not answerable with a simple “yes” or “no,” but rather requires synthesis and analysis of ideas and sources prior to composition of an answer.
- arguable : its potential answers are open to debate rather than accepted facts.
You should ask a question about an issue that you are genuinely curious and/or passionate about.
The question you ask should be developed for the discipline you are studying. A question appropriate for Biology, for instance, is different from an appropriate one in Political Science or Sociology. If you are developing your question for a course other than first-year composition, you may want to discuss your ideas for a research question with your professor.
Why is a research question essential to the research process? Research questions help writers focus their research by providing a path through the research and writing process. The specificity of a well-developed research question helps writers avoid the “all-about” paper and work toward supporting a specific, arguable thesis.
Steps to developing a research question:
- Choose an interesting general topic. Most professional researchers focus on topics they are genuinely interested in studying. Writers should choose a broad topic about which they genuinely would like to know more. An example of a general topic might be “Slavery in the American South” or “Films of the 1930s.”
- Do some preliminary research on your general topic. Do a few quick searches in current periodicals and journals on your topic to see what’s already been done and to help you narrow your focus. What issues are scholars and researchers discussing, when it comes to your topic? What questions occur to you as you read these articles?
- Consider your audience. For most college papers, your audience will be academic, but always keep your audience in mind when narrowing your topic and developing your question. Would that particular audience be interested in the question you are developing?
- Start asking questions. Taking into consideration all of the above, start asking yourself open-ended “how” and “why” questions about your general topic. For example, “Why were slave narratives effective tools in working toward the abolishment of slavery?” or “How did the films of the 1930s reflect or respond to the conditions of the Great Depression?”
- Is your research question clear? With so much research available on any given topic, research questions must be as clear as possible in order to be effective in helping the writer direct his or her research.
- Is your research question focused? Research questions must be specific enough to be well covered in the space available.
- Is your research question complex? Research questions should not be answerable with a simple “yes” or “no” or by easily-found facts. They should, instead, require both research and analysis on the part of the writer. They often begin with “How” or “Why.”
- Begin your research . After you’ve come up with a question, think about the possible paths your research could take. What sources should you consult as you seek answers to your question? What research process will ensure that you find a variety of perspectives and responses to your question?
Sample Research Questions
Unclear: How should social networking sites address the harm they cause? Clear: What action should social networking sites like MySpace and Facebook take to protect users’ personal information and privacy? The unclear version of this question doesn’t specify which social networking sites or suggest what kind of harm the sites might be causing. It also assumes that this “harm” is proven and/or accepted. The clearer version specifies sites (MySpace and Facebook), the type of potential harm (privacy issues), and who may be experiencing that harm (users). A strong research question should never leave room for ambiguity or interpretation. Unfocused: What is the effect on the environment from global warming? Focused: What is the most significant effect of glacial melting on the lives of penguins in Antarctica?
The unfocused research question is so broad that it couldn’t be adequately answered in a book-length piece, let alone a standard college-level paper. The focused version narrows down to a specific effect of global warming (glacial melting), a specific place (Antarctica), and a specific animal that is affected (penguins). It also requires the writer to take a stance on which effect has the greatest impact on the affected animal. When in doubt, make a research question as narrow and focused as possible.
Too simple: How are doctors addressing diabetes in the U.S.? Appropriately Complex: What main environmental, behavioral, and genetic factors predict whether Americans will develop diabetes, and how can these commonalities be used to aid the medical community in prevention of the disease?
The simple version of this question can be looked up online and answered in a few factual sentences; it leaves no room for analysis. The more complex version is written in two parts; it is thought provoking and requires both significant investigation and evaluation from the writer. As a general rule of thumb, if a quick Google search can answer a research question, it’s likely not very effective.
Last updated 8/8/2018

The Writing Center --> --> --> --> --> --> --> --> -->
4400 University Drive, 2G8 Fairfax, VA 22030
- Johnson Center, Room 227E
- +1-703-993-1200
- [email protected]
Quick Links
- Register with us
© Copyright 2024 George Mason University . All Rights Reserved. Privacy Statement | Accessibility

IMAGES
COMMENTS
To recap, the 8 steps to writing a quality dissertation (or thesis) are as follows: Understand what a dissertation (or thesis) is – a research project that follows the research process. Find a unique (original) and important research topic; Craft a convincing dissertation or thesis research proposal; Write a clear, compelling introduction chapter
Oct 30, 2022 · The first question asks for a ready-made solution, and is not focused or researchable. The second question is a clearer comparative question, but note that it may not be practically feasible. For a smaller research project or thesis, it could be narrowed down further to focus on the effectiveness of drunk driving laws in just one or two countries.
Aug 13, 2021 · A research question example is a sample that provides a deeper understanding of how to write a research question. These examples can help first-time authors comprehend the structure and components of the question. A research question’s length depends on the topic chosen and the specific requirements of the field.
Oct 30, 2022 · A research question pinpoints exactly what you want to find out in your work. A good research question is essential to guide your research paper, dissertation, or thesis. All research questions should be: Focused on a single problem or issue; Researchable using primary and/or secondary sources; Feasible to answer within the timeframe and ...
Aug 8, 2018 · Why is a research question essential to the research process? Research questions help writers focus their research by providing a path through the research and writing process. The specificity of a well-developed research question helps writers avoid the “all-about” paper and work toward supporting a specific, arguable thesis.
These questions are not separate research questions as much as they are questions that the researcher will use to guide an analysis of the data. They are methodological guidelines that will help in the coding of the data. Remember that a research question is what the dissertation is about. It produces the title of the dissertation.